History Of Jacksonville, Florida on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The city of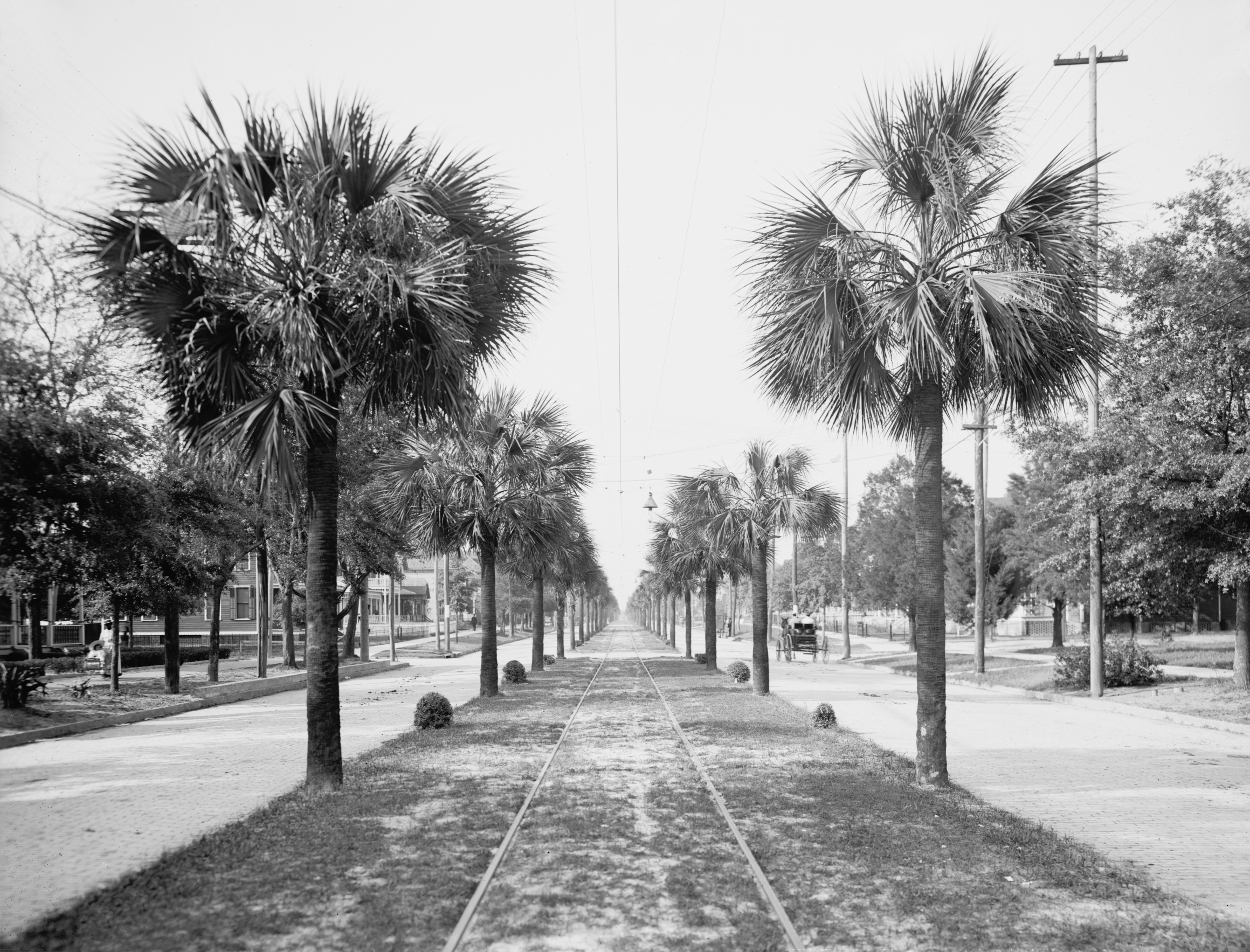 
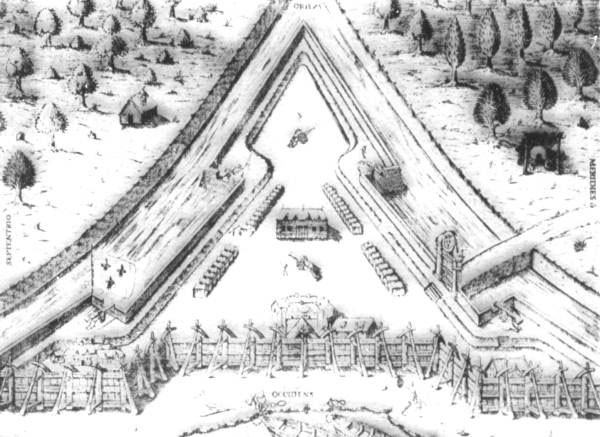 In 1513,
In 1513,
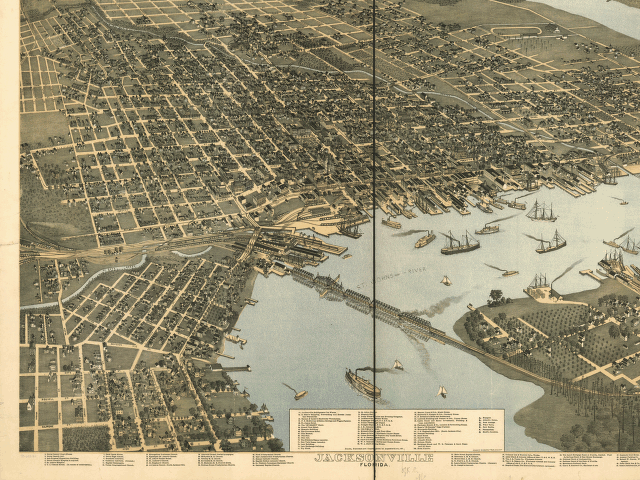 Following the
Following the
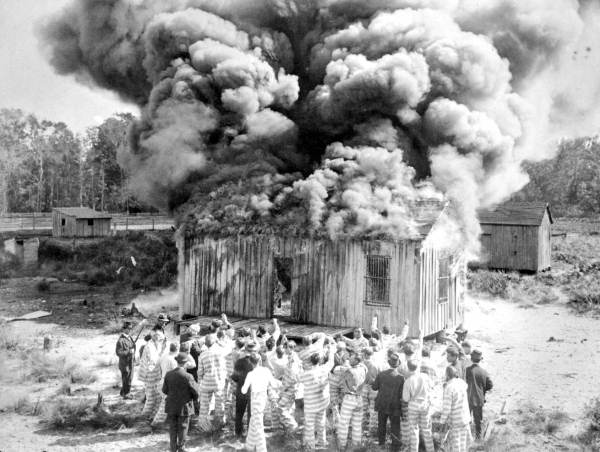 In the early 20th century, before
In the early 20th century, before
 The 1920s brought significant real estate development and speculation to the city during the great
The 1920s brought significant real estate development and speculation to the city during the great
 A significant part of Jacksonville's growth in the 20th century came from the presence of navy bases in the region. October 15, 1940,
A significant part of Jacksonville's growth in the 20th century came from the presence of navy bases in the region. October 15, 1940,
"Offshore Power Systems: Big Plants for a Big Customer"
Atomic Insights, August 1996Putnam, Walter
"Floating nuclear plants may become reality"
Boca Raton News, November 15, 1981 Construction of the new facility was projected to cost $200 million and create 10,000 new jobs when completed in 1976."Urban waterfront lands"
Page 136, National Research Council Committee, 1980 Contracts were signed by
“ALEXANDER P. 'ZEKE' ZECHELLA: 1920-2009”
Florida Times-Union, August 18, 2009 OPS obtained 850+ acres (3.4 km2) on
online edition
Photographic exhibit on the Great Fire of 1901; presented by the State Archives of Florida.
The Jacksonville Historical Society
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Jacksonville, Florida
Jacksonville, Florida
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the seat of Duval County, with which the ...
, began to grow in the late 18th century as Cow Ford, settled by British colonists. Its major development occurred in the late nineteenth century, when it became a winter vacation destination for tourists from the North and Midwest. Its development was halted or slowed by the Great Fire of 1901
The Great Fire of 1901 was a conflagration that occurred in Jacksonville, Florida on May 3, 1901. It was one of the worst disasters in Florida history and the third largest urban fire in the U.S., next to the Great Chicago Fire, and the 1906 S ...
, the Florida Land Bust of the 1920s, and the economic woes of the 1960s and 70s. Since the late 20th century, the city has experienced steady growth, with a new federal building constructed in downtown in 2003.
Since 1940, Jacksonville has also been a major port for the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
. The city is a thriving metropolis with over a million citizens. Due to its consolidated city-county
In United States local government, a consolidated city-county is formed when one or more cities and their surrounding county ( parish in Louisiana, borough in Alaska) merge into one unified jurisdiction. As such it has the governmental powers o ...
government structure, it has the largest municipal population among Florida cities, as well as the largest land area of any city in the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
.

Early days
Ancient history
Archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
evidence indicates 6,000 years of human habitation in the area. Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and por ...
has been found dating to 2500 BC, nearly the oldest in the United States and second to artifacts of the Savannah River
The Savannah River is a major river in the southeastern United States, forming most of the border between the states of South Carolina and Georgia. Two tributaries of the Savannah, the Tugaloo River and the Chattooga River, form the norther ...
area. In the 16th century, the beginning of the historical record period, the area was inhabited by the Mocama
The Mocama were a Native American people who lived in the coastal areas of what are now northern Florida and southeastern Georgia. A Timucua group, they spoke the dialect known as Mocama, the best-attested dialect of the Timucua language. Their t ...
, a coastal subgroup of the Timucua
The Timucua were a Native American people who lived in Northeast and North Central Florida and southeast Georgia. They were the largest indigenous group in that area and consisted of about 35 chiefdoms, many leading thousands of people. The var ...
indigenous Native Americans. At the time of contact with Europeans, most Mocama villages in present-day Jacksonville were part of the powerful chiefdom known as the Saturiwa
The Saturiwa were a Timucua chiefdom centered on the mouth of the St. Johns River in what is now Jacksonville, Florida. They were the largest and best attested chiefdom of the Timucua subgroup known as the Mocama, who spoke the Mocama dialect of ...
, centered on Fort George Island
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
near the mouth of the St. Johns River
The St. Johns River ( es, Río San Juan) is the longest river in the U.S. state of Florida and its most significant one for commercial and recreational use. At long, it flows north and winds through or borders twelve counties. The drop in eleva ...
. They had a complex society, well-adapted to the environmental conditions of the area.
Colonial and territorial history
 In 1513,
In 1513, Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
explorers landed in Florida and claimed their discovery for Spain (see Spanish Florida
Spanish Florida ( es, La Florida) was the first major European land claim and attempted settlement in North America during the European Age of Discovery. ''La Florida'' formed part of the Captaincy General of Cuba, the Viceroyalty of New Spain, ...
). The first Europeans to visit the area were Spanish missionaries
A missionary is a member of a religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Mi ...
and explorers from this period. In February 1562, French naval officer Jean Ribault
Jean Ribault (also spelled ''Ribaut'') (1520 – October 12, 1565) was a French naval officer, navigator, and a colonizer of what would become the southeastern United States. He was a major figure in the French attempts to colonize Florida. A H ...
and a 150 settlers arrived seeking land for a safe haven for the French Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Be ...
s, Protestants suffering religious persecution in France. Ribault explored the mouth of the St. Johns River
The St. Johns River ( es, Río San Juan) is the longest river in the U.S. state of Florida and its most significant one for commercial and recreational use. At long, it flows north and winds through or borders twelve counties. The drop in eleva ...
before moving north and establishing the colony of Charlesfort
The Charlesfort-Santa Elena Site is an important early colonial archaeological site on Parris Island, South Carolina. It contains the archaeological remains of a French settlement called Charlesfort, settled in 1562 and abandoned the following y ...
on what is now Parris Island, South Carolina
Parris Island is a district of the city of Port Royal, South Carolina on an island of the same name. It became part of the city with the annexation of the Marine Corps Recruit Depot Parris Island on October 11, 2002. For statistical purposes, the ...
. Ribault returned to France for supplies, but tensions from French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the term which is used in reference to a period of civil war between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants, commonly called Huguenots, which lasted from 1562 to 1598. According to estim ...
had broken out during his absence. His return to Florida was delayed as a result. Without leadership or provisions, the colonists abandoned Charlesfort. In 1564 Ribault's former lieutenant, René Goulaine de Laudonnière
Rene Goulaine de Laudonnière (c. 1529–1574) was a French Huguenot explorer and the founder of the French colony of Fort Caroline in what is now Jacksonville, Florida. Admiral Gaspard de Coligny, a Huguenot, sent Jean Ribault and Laudonnière ...
, launched a new expedition to found a colony on the St. Johns River. On June 22, 1564, the settlers established Fort Caroline
Fort Caroline was an attempted French colonial settlement in Florida, located on the banks of the St. Johns River in present-day Duval County. It was established under the leadership of René Goulaine de Laudonnière on 22 June, 1564, followin ...
atop the St. Johns Bluff.
Laudonnière made an alliance with the local tribe of Timucua
The Timucua were a Native American people who lived in Northeast and North Central Florida and southeast Georgia. They were the largest indigenous group in that area and consisted of about 35 chiefdoms, many leading thousands of people. The var ...
Indians, the Saturiwa
The Saturiwa were a Timucua chiefdom centered on the mouth of the St. Johns River in what is now Jacksonville, Florida. They were the largest and best attested chiefdom of the Timucua subgroup known as the Mocama, who spoke the Mocama dialect of ...
. He also forged friendly relations with their competitors, the Utina tribe, who lived upriver to the south (around what is now Palatka and the Lake George area). Ribault intended to resupply Fort Caroline in early 1565, but was again delayed. As a result, the colony faced famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
, three mutinies
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military, of a crew or of a crew of pirates) to oppose, change, or overthrow an organization to which they were previously loyal. The term is commonly used for a rebellion among member ...
, and eventually warfare with the Utina. Ribault finally reached the fort with a relief expedition in the summer, and assumed command of the settlement. In the meantime, the Spanish admiral Pedro Menéndez de Avilés had established the colony of St. Augustine 35 miles to the south, with the express mission to displace the French.
When he arrived, Ribault launched a naval expedition of 200 sailors and 400 soldiers to dislodge the Spanish, but a storm at sea incapacitated them for several days and caused numerous deaths. On September 20, 1565, Menéndez marched his men overland to Fort Caroline, defended by 200 or 250 people, and killed everyone except for 50 women and children and 26 men who escaped. The Spanish picked up the survivors of Ribault's fleet, and summarily executed all but 20.
The Spanish took over Fort Caroline, renaming it as San Matteo. In 1568 the French and Spanish confronted each other again here, when Dominique de Gourgues
Dominique (or Domingue) de Gourgues (1530–1593) was a French nobleman and soldier. He is best known for leading an attack against Spanish Florida in 1568, in response to the destruction of the French Fort Caroline. He was a captain in King Cha ...
burned it to the ground. The Spanish rebuilt the fort, but abandoned it in 1569. The Spanish next built Fort San Nicolas further upriver to protect the rear flank of St. Augustine. "San Nicolas" served as their name for the Jacksonville area, a placename which survives in the neighborhood of St. Nicholas. The fort was located on the east side of the St. Johns, where Bishop Kenny High School
Bishop Kenny High School (commonly referred to as Bishop Kenny or BKHS) is a private, college-preparatory, coeducational Catholic high school in Jacksonville, Florida. It is located in and administered by the Roman Catholic Diocese of St. August ...
now stands. The fort was abandoned in the late 17th century.
France and Spain were defeated by the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
in the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
. During the war the British had defeated the Spanish in Cuba and occupied the island, whereas Florida had hardly seen any fighting. As part of the negotiations between the two nations in the aftermath of the war, Spain would cede Florida to Great Britain in exchange for the return of Cuba. The British agreed and Florida was ceded to the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
in 1763. The British soon constructed the King's Road connecting St. Augustine to Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
. The road crossed the St. Johns River at a narrow point, which the Seminole
The Seminole are a Native American people who developed in Florida in the 18th century. Today, they live in Oklahoma and Florida, and comprise three federally recognized tribes: the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, the Seminole Tribe of Florida, an ...
called ''Wacca Pilatka'' and the British named the "Cow Ford", both names ostensibly reflecting the fact that cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult mal ...
were brought across the river there. The British divided Florida into the two colonies of British East Florida
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and British West Florida
British West Florida was a colony of the Kingdom of Great Britain from 1763 until 1783, when it was ceded to Spain as part of the Peace of Paris.
British West Florida comprised parts of the modern U.S. states of Louisiana, Mississippi, Alab ...
.
The British government gave land grants to officers and soldiers who had fought in the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
in order to encourage settlement. In order to induce settlers to move to the two new colonies reports of Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
's natural wealth were published in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
. A large number of British colonists who were "energetic and of good character" moved to Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
, mostly coming from South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
and England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
though there was also a group of settlers who came from the colony of Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = " Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, e ...
. This would be the first permanent English-speaking population in what is now Duval County, Baker County, St. Johns County and Nassau County. The British built good public roads and introduced the cultivation of sugar cane, indigo and fruits as well the export of lumber. As a result of these initiatives northeastern Florida prospered economically in a way it never did under Spanish rule. Furthermore, the British governors were directed to call general assemblies as soon as possible in order to make laws for the Floridas and in the meantime they were, with the advice of councils, to establish courts. This would be the first introduction of much of the English-derived legal system which Florida still has today including trial-by-jury, habeas corpus
''Habeas corpus'' (; from Medieval Latin, ) is a recourse in law through which a person can report an unlawful detention or imprisonment to a court and request that the court order the custodian of the person, usually a prison official, t ...
and county-based government.
The British gave control of the territory back to Spain in 1783. Americans of English descent and Americans of Scots-Irish descent began moving into northern Florida from the backwoods of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
and South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
. Though technically not allowed by the Spanish authorities, the Spanish were never able to effectively police the border region and the backwoods settlers from the United States would continue to migrate into Florida unchecked. These migrants, mixing with the already present English-speaking settlers who had lived in Florida since the British period, would be the progenitors of the population known as Florida Cracker
Florida crackers were colonial-era British and American pioneer settlers in what is now the U.S. state of Florida; the term is also applied to their descendants, to the present day, and their subculture among white Southerners. The first cracke ...
s. The Spanish also accepted fugitive slaves
In the United States, fugitive slaves or runaway slaves were terms used in the 18th and 19th century to describe people who fled slavery. The term also refers to the federal Fugitive Slave Acts of 1793 and 1850. Such people are also called free ...
from the newly-created United States if they accepted Catholic baptism.
Between 1812 and 1814 during the War of 1812 between the US and Britain, the US Navy assisted American settlers in Florida in "The Patriot War", a covert attempt to seize control of Florida from the Spanish. They began with invasions of Fernandina and Amelia Island. Spain sold the Florida Territory
The Territory of Florida was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 30, 1822, until March 3, 1845, when it was admitted to the Union as the state of Florida. Originally the major portion of the Spanish te ...
to the United States in 1821 and, by 1822, Jacksonville's current name had come into use, to honor General Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
. It first appears on a petition sent on June 15, 1822 to U.S. Secretary of State
The United States secretary of state is a member of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States and the head of the U.S. Department of State. The office holder is one of the highest ranking members of the president's Ca ...
John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, and diarist who served as the sixth president of the United States, from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States S ...
, asking that Jacksonville be named a port of entry
In general, a port of entry (POE) is a place where one may lawfully enter a country. It typically has border security staff and facilities to check passports and visas and to inspect luggage to assure that contraband is not imported. Internati ...
. The city is named for Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
, military governor
A military government is generally any form of government that is administered by military forces, whether or not this government is legal under the laws of the jurisdiction at issue, and whether this government is formed by natives or by an occup ...
of the Florida Territory and eventual President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
of the United States. U.S. settlers led by Isaiah D. Hart
Isaiah David Hart (November 6, 1792 – September 4, 1861) was an American plantation owner, and the founder of Jacksonville, Florida. Originally from Georgia, Hart took up arms against Spain in the Patriot Rebellion of 1812. After moving to a lo ...
wrote a charter for a town government, which was approved by the Florida Legislative Council on February 9, 1832. Remembered as the city's most important founding father, Hart is memorialized with the Isaiah D. Hart Bridge over the St. Johns.
Civil War
Even before the outbreak of war, a militia unit was raised in Jacksonville in April of 1859. The unit, called the Jacksonville Light Infantry, would become Company A of the 3rd Florida Infantry Regiment. The company carried a battle flag bearing the slogan "Let Us Alone" and was commanded by Dr. Holmes Steele, a former mayor of the city. During theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, Jacksonville was a key supply point for hogs and cattle leaving Florida and aiding the Confederate
Confederacy or confederate may refer to:
States or communities
* Confederate state or confederation, a union of sovereign groups or communities
* Confederate States of America, a confederation of secessionist American states that existed between 1 ...
cause. Throughout most of the war, the US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of ...
maintained a blockade around Florida's ports, including Jacksonville. In October 1862 Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
forces captured a Confederate battery in the Battle of St. Johns Bluff
The Battle of St. John's Bluff was fought from October 1–3, 1862, between Union and Confederate forces in Duval County, Florida, during the American Civil War. The battle resulted in a significant Union victory, helping secure their control o ...
and occupied Jacksonville. Throughout the war Jacksonville changed hands several times, though never with a battle. On February 20, 1864, Union soldiers from Jacksonville marched inland and confronted the Confederate Army at the Battle of Olustee
The Battle of Olustee or Battle of Ocean Pond was fought in Baker County, Florida on February 20, 1864, during the American Civil War. It was the largest battle fought in Florida during the war.
Union General Truman Seymour had landed troops a ...
.
The battle was a devastating loss for the Union and a decisive victory for the Confederacy. Soldiers on both sides were veterans of the great battles in the eastern and western theaters of war, but many of them remarked in letters and diaries that they had never experienced such terrible fighting. The Confederate dead were buried at Oaklawn Cemetery in nearby Lake City. The Union losses caused Northern authorities to question the necessity of further Union involvement in the militarily insignificant region of northern Florida. On the morning of 22 February, as the Union forces were still retreating to Jacksonville, the 54th Massachusetts was ordered to counter-march back to Ten-Mile Station. The locomotive of a train carrying wounded Union soldiers had broken down and the wounded were in danger of capture. When the 54th Massachusetts arrived, the men attached ropes to the engine and cars and manually pulled the train approximately three miles to Camp Finnegan, where horses were secured to help pull the train. After that, the train was pulled by both men and horses to Jacksonville for a total distance of ten miles. It took forty-two hours to pull the train that distance.
The US Transport Maple Leaf was sunk at Jacksonville, April 1, 1864.
The U.S. Transport General Hunter was sunk in the St. John's River, April 16, 1864, close to where the Maple Leaf was sunk.
In the fall of 1865, a black enlisted man in the 3rd USCT was hung by his thumbs for stealing from a field kitchen. The punishment led to a riot and gunfire was exchanged between black enlisted men and their white officers. The riot was put down and several soldiers were put on trial for mutiny, with 6 of them being executed.
By the end of the war in 1865, a Union commander commented that Jacksonville had become "pathetically dilapidated, a mere skeleton of its former self, a victim of war."
Post Civil War
Winter resort era
 Following the
Following the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, during Reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
*Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*'' Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Unio ...
and afterward, Jacksonville and nearby St. Augustine became popular winter resorts for the rich and famous of the Gilded Age
In United States history, the Gilded Age was an era extending roughly from 1877 to 1900, which was sandwiched between the Reconstruction era and the Progressive Era. It was a time of rapid economic growth, especially in the Northern and Weste ...
. Visitors arrived by steamboat
A steamboat is a boat that is marine propulsion, propelled primarily by marine steam engine, steam power, typically driving propellers or Paddle steamer, paddlewheels. Steamboats sometimes use the ship prefix, prefix designation SS, S.S. or S/S ...
and (beginning in the 1880s) by railroad
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
, and wintered at dozens of hotels and boarding houses. The 1888 Subtropical Exposition
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north an ...
was held in Jacksonville and attended by President Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland (March 18, 1837June 24, 1908) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 22nd and 24th president of the United States from 1885 to 1889 and from 1893 to 1897. Cleveland is the only president in American ...
, but the Florida-style world's fair did not lead to a lasting boost for tourism in Jacksonville. The area declined in importance as a resort destination after Henry Flagler
Henry Morrison Flagler (January 2, 1830 – May 20, 1913) was an American industrialist and a founder of Standard Oil, which was first based in Ohio. He was also a key figure in the development of the Atlantic coast of Florida and founde ...
extended the Florida East Coast Railroad
The Florida East Coast Railway is a Class II railroad operating in the U.S. state of Florida, currently owned by Grupo México.
Built primarily in the last quarter of the 19th century and the first decade of the 20th century, the FEC was a pro ...
to the south, reaching Palm Beach in 1894 and the Miami area in 1896. This drew tourism to the southern Atlantic Coast.
Yellow fever epidemics
Jacksonville's prominence as a winter resort was dealt another blow by majoryellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. In ...
epidemics in 1886 and 1888. During the second one, nearly ten percent of the more than 4,000 victims died, including the city's mayor. In the absence of scientific knowledge concerning the cause of yellow fever, nearly half (10,000 out of 25,000) of the city's panicked residents fled despite the imposition of quarantine
A quarantine is a restriction on the movement of people, animals and goods which is intended to prevent the spread of disease or pests. It is often used in connection to disease and illness, preventing the movement of those who may have been ...
s. Inbound and outbound mail was fumigated in an effort to reduce contagion. Jacksonville's reputation as a healthful tourist destination suffered. The African-American population did not appear to catch the disease, leading the panicked population into erroneously believing that the black residents were "carriers" of the Yellow Fever. In fact, blacks had immunity from catching the disease earlier, as children.
Spanish–American War
During theSpanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (clock ...
, gunrunners helping the Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
n rebels used Jacksonville as the center for smuggling illegal arms and supplies to the island. Duval County sheriff and future state governor, Napoleon Bonaparte Broward
Napoleon Bonaparte Broward (April 19, 1857 – October 1, 1910) was an American river pilot, captain, and politician. He was elected as the 19th governor of the U.S. state of Florida, serving from January 3, 1905, to January 5, 1909. He was mos ...
, was one of the many gunrunners operating out of the city. Author Stephen Crane
Stephen Crane (November 1, 1871 – June 5, 1900) was an American poet, novelist, and short story writer. Prolific throughout his short life, he wrote notable works in the Realist tradition as well as early examples of American Naturalism an ...
travelled to Jacksonville to cover the war.
20th century
Great Fire of 1901
On May 3, 1901, downtown Jacksonville was ravaged by the Great Fire—the largest-ever urban fire in theSoutheastern United States
The Southeastern United States, also referred to as the American Southeast or simply the Southeast, is a geographical region of the United States. It is located broadly on the eastern portion of the southern United States and the southern por ...
, which started when hot ash from a shantyhouse's chimney landed on the drying moss at Cleaveland's Fiber Factory. At half past noon most of the Cleaveland workers were at lunch, but by the time they returned the entire city block was engulfed in flames. The fire destroyed the business district and rendered 10,000 residents homeless in the course of eight hours. Florida Governor William S. Jennings declared a state of martial law
Martial law is the imposition of direct military control of normal civil functions or suspension of civil law by a government, especially in response to an emergency where civil forces are overwhelmed, or in an occupied territory.
Use
Marti ...
in Jacksonville and dispatched several state militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
units to help. Reconstruction started immediately, and the city was returned to civil authority on May 17. Despite the widespread damage, only seven deaths were reported.
Young architect Henry John Klutho
Henry John Klutho (1873–1964) was an American architect known for his work in the "Prairie School" style. He helped in the reconstruction of Jacksonville, Florida after the Great Fire of 1901—the largest-ever urban fire in the Southeast—by ...
had just returned to New York from a year in Europe when he read about the Jacksonville fire and, seeing a rare opportunity, he headed south. Klutho and other architects, enamored by the "Prairie Style
Prairie School is a late 19th- and early 20th-century architectural style, most common in the Midwestern United States. The style is usually marked by horizontal lines, flat or hip roof, hipped roofs with broad Overhang (architecture), ove ...
" of architecture then being popularized by architect Frank Lloyd Wright
Frank Lloyd Wright (June 8, 1867 – April 9, 1959) was an American architect, designer, writer, and educator. He designed more than 1,000 structures over a creative period of 70 years. Wright played a key role in the architectural movements o ...
in Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
and other Midwestern cities, designed exuberant local buildings with a Florida flair. While many of Klutho's buildings were demolished by the 1980s, a number of his creations remain, including the St. James Building from 1911 (a former department store that is now Jacksonville's City Hall) and the Morocco Temple from 1910. The Klutho Apartments, in Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
, were recently restored and converted into office space by local charity Fresh Ministries
FreshMinistries is a non-profit organization based in Jacksonville, Florida which goal is to eradicate poverty, improve race relations and build stronger communities. The group focuses on economic development, job training and health initiatives ...
. Despite the losses of the last several decades, Jacksonville still has one of the largest collections of Prairie Style buildings (particularly residences) outside the Midwest.
Motion picture industry
 In the early 20th century, before
In the early 20th century, before Hollywood
Hollywood usually refers to:
* Hollywood, Los Angeles, a neighborhood in California
* Hollywood, a metonym for the cinema of the United States
Hollywood may also refer to:
Places United States
* Hollywood District (disambiguation)
* Hollywood, ...
, the motion picture industry was based in Fort Lee, New Jersey
Fort Lee is a borough at the eastern border of Bergen County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey, situated along the Hudson River atop the Palisades.
As of the 2020 U.S. census, the borough's population was 40,191. As of the 2010 U.S. census, th ...
. In need of a winter headquarters, moviemakers were attracted to Jacksonville due to its warm climate, exotic locations, excellent rail access, and cheaper labor, earning the city the title of "The Winter Film Capital of the World." New York-based Kalem Studios
The Kalem Company was an early American film studio founded in New York City in 1907. It was one of the first companies to make films abroad and to set up winter production facilities, first in Florida and then in California. Kalem was sold to V ...
was the first to open a permanent studio in Jacksonville in 1908. Over the course of the next decade, more than 30 silent film companies established studios in town, including Metro Pictures
Metro Pictures Corporation was a Film, motion picture production company founded in early 1915 in Jacksonville, Florida. It was a forerunner of Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer. The company produced its films in New York, Los Angeles, and sometimes at leas ...
(later MGM
Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Studios Inc., also known as Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Pictures and abbreviated as MGM, is an American film, television production, distribution and media company owned by Amazon through MGM Holdings, founded on April 17, 1924 a ...
), Edison Studios
Edison Studios was an American film production organization, owned by companies controlled by inventor and entrepreneur, Thomas Edison. The studio made close to 1,200 films, as part of the Edison Manufacturing Company (1894–1911) and then Thom ...
, Majestic Films, King Bee Film Company, Vim Comedy Company, Norman Studios, Gaumont Studios and the Lubin Manufacturing Company
The Lubin Manufacturing Company was an American motion picture production company that produced silent films from 1896 to 1916. Lubin films were distributed with a Liberty Bell trademark.
History
The Lubin Manufacturing Company was formed in 1 ...
. Comedic actor and Georgia native Oliver ''"Babe"'' Hardy began his motion picture career here in 1914. He starred in over 36 short silent films his first year acting. With the closing of Lubin in early 1915, Oliver moved to New York then New Jersey to find film jobs. Acquiring a job with the Vim Company in early 1915, he returned to Jacksonville
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the List of United States cities by area, largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the co ...
in the spring of 1917 before relocating to Los Angeles in October 1917. The first motion picture made in Technicolor
Technicolor is a series of Color motion picture film, color motion picture processes, the first version dating back to 1916, and followed by improved versions over several decades.
Definitive Technicolor movies using three black and white films ...
and the first feature-length color movie produced in the United States, ''The Gulf Between
''The Gulf Between'' is a 1917 American comedy-drama film that was the first motion picture made in Technicolor, the fourth feature-length color film, and the first feature-length color film produced in the United States. The film was destroyed in ...
'', was also filmed on location in Jacksonville in 1917.
Jacksonville was especially important to the African American film industry. One notable individual in this regard is the European American producer Richard Norman, who created a string of films starring black actors in the vein of Oscar Micheaux
Oscar Devereaux Micheaux (; January 2, 1884 – March 25, 1951) was an author, film director and independent producer of more than 44 films. Although the short-lived Lincoln Motion Picture Company was the first movie company owned and controlled ...
and the Lincoln Motion Picture Company. In contrast to the degrading parts offered in certain white films such as ''The Birth of a Nation
''The Birth of a Nation'', originally called ''The Clansman'', is a 1915 American silent epic drama film directed by D. W. Griffith and starring Lillian Gish. The screenplay is adapted from Thomas Dixon Jr.'s 1905 novel and play ''The Cla ...
'', Norman and his contemporaries sought to create positive stories featuring African Americans in what he termed "splendidly assuming different roles."
Jacksonville's mostly conservative residents, however, objected to the hallmarks of the early movie industry, such as car chases in the streets, simulated bank robberies and fire alarms in public places, and even the occasional riot. In 1917, conservative Democrat John W. Martin
John Wellborn Martin (June 21, 1884 – February 22, 1958) was an American politician who served as the List of Governors of Florida, 24th Governor of Florida, from 1925 to 1929. He also served as Mayor of Jacksonville, Mayor of Jacksonville, Flo ...
was elected mayor on the platform of taming the city's movie industry. By that time, southern California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
was emerging as the major movie production center, thanks in large part to the move of film pioneers like William Selig
William Nicholas Selig (March 14, 1864 – July 15, 1948) was a pioneer of the American motion picture industry. In 1896 he created one of the first film production companies, Selig Polyscope Company of Chicago. Selig produced a string of c ...
and D.W. Griffith
David Wark Griffith (January 22, 1875 – July 23, 1948) was an American film director. Considered one of the most influential figures in the history of the motion picture, he pioneered many aspects of film editing and expanded the art of the na ...
to the area. These factors quickly sealed the demise of Jacksonville as a major film destination.
"Gateway to Florida"
 The 1920s brought significant real estate development and speculation to the city during the great
The 1920s brought significant real estate development and speculation to the city during the great Florida land boom
The Florida land boom of the 1920s was Florida's first real estate bubble. This pioneering era of Florida land speculation lasted from 1924 to 1926 and attracted investors from all over the nation. The land boom left behind entirely new, planned ...
(and bust). Hordes of train passengers passed through Jacksonville on their way south to the new tourist destinations of South Florida, as most of the passenger trains arriving from the population centers of the North were routed through Jacksonville.
The Riverside Theater, which opened in 1927,http://www.waymarking.com/waymarks/WM3DHH Waymarking, Five Points Theater, Jacksonville
was the first theater in Florida to show talking pictures
A sound film is a motion picture with synchronized sound, or sound technologically coupled to image, as opposed to a silent film. The first known public exhibition of projected sound films took place in Paris in 1900, but decades passed before ...
.
Completion of the Dixie Highway
Dixie Highway was a United States auto trail first planned in 1914 to connect the Midwest with the South. It was part of a system and was expanded from an earlier Miami to Montreal highway. The final system is better understood as a network of ...
(portions of which became U.S. 1) in the 1920s began to draw significant automobile traffic as well. An important entry point to the state since the 1870s, Jacksonville now justifiably billed itself as the "Gateway to Florida."
US Navy
Naval Air Station Jacksonville
Naval Air Station Jacksonville (NAS Jacksonville) is a large naval air station located approximately eight miles (13 km) south of the central business district of Jacksonville, Florida, United States., effective 2007-10-25
Location
NAS Jack ...
("NAS Jax") on the westside became the first navy installation in the city. This base was a major training center during World War II, with over 20,000 pilots and aircrewmen being trained there. After the war, the Navy's elite Blue Angels
The Blue Angels is a flight demonstration squadron of the United States Navy.
were established at NAS Jax. Today NAS Jax is the third largest navy installation in the country and employs over 23,000 civilian and active-duty personnel.
In June 1941, land in the westernmost side of Duval County was earmarked for a second naval air facility. This became NAS Cecil Field, which during the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
was designated a Master Jet Base
In the United States Navy, a master jet base is a naval air station with permanent basing and homeporting of carrier-based tactical jet squadrons (e.g., fighter, strike fighter, attack), carrier air wings, and the provision of one or more jet-cap ...
, the only one in the South. RF-8 Crusaders out of Cecil Field detected missiles in Cuba, precipitating the Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis, also known as the October Crisis (of 1962) ( es, Crisis de Octubre) in Cuba, the Caribbean Crisis () in Russia, or the Missile Scare, was a 35-day (16 October – 20 November 1962) confrontation between the United S ...
. In 1993, the Navy decided to close NAS Cecil Field, and this was completed in 1999. The land once occupied by this installation is now known as the "Cecil Commerce Center" and contains one of the campuses of Florida Community College which now offers civil aeronautics classes.
December 1942 saw the addition of a third naval installation to Jacksonville: Naval Station Mayport
Naval Station Mayport is a major United States Navy base in Jacksonville, Florida. It contains a protected harbor that can accommodate aircraft carrier-size vessels, ship's intermediate maintenance activity (SIMA) and a military airfield (Admi ...
at the mouth of the St. Johns River. This port developed through World War II and today is the home port for many types of navy ships, most notably the aircraft carrier from 1995 to 26 July 2007, when Big John was towed away, eventually to be mothballed in Philadelphia (see more at https://web.archive.org/web/20071012152907/http://jacksonville.com/usskennedy/). NS Mayport current employs about 14,000 personnel.
Jacksonville is also not far from Naval Submarine Base Kings Bay
Naval Submarine Base Kings Bay is a base of the United States Navy located adjacent to the city of St. Marys in Camden County, Georgia, on the North River in southeastern Georgia, and 38 miles (61 km) from Jacksonville, Florida. The Submari ...
in St. Marys, Georgia, which is home to part of the US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of ...
's nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN
A ballistic missile submarine is a submarine capable of deploying submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) with nuclear warheads. The United States Navy's hull classification symbols for ballistic missile submarines are SSB and SSBN – ...
) fleet.
The naval base became a key training ground in the 1950s and 1960s and as such, the population of the city rose dramatically. More than half of the residents in Jacksonville had some tie to the naval base, whether it be a relative stationed there, or due to employment opportunities, by 1970, necessitating the opening of an international airport
An international airport is an airport with customs and border control facilities enabling passengers to travel between countries around the world. International airports are usually larger than domestic airports and they must feature longer ...
in the area.
Hotel Roosevelt fire
On December 29, 1963, a fire gutted the first couple of stories of the Hotel Roosevelt on Adams Street, killing 22 people, setting a record for the highest one-day death toll in Jacksonville history. The hotel was later abandoned, with most businesses inside moving to the nearby Hotel George Washington.Floating nuclear power plants
Offshore Power Systems (OPS) was a 1970 joint venture betweenWestinghouse Electric Company
Westinghouse Electric Company LLC is an American nuclear power company formed in 1999 from the nuclear power division of the original Westinghouse Electric Corporation. It offers nuclear products and services to utilities internationally, includi ...
, who constructed nuclear generating plants, and Newport News Shipbuilding and Drydock
Newport News Shipbuilding (NNS), a division of Huntington Ingalls Industries, is the largest industrial employer in Virginia, and sole designer, builder and refueler of United States Navy aircraft carriers and one of two providers of U.S. Navy ...
, who had recently merged with Tenneco
Tenneco (formerly Tenneco Automotive and originally Tennessee Gas Transmission Company) is an American automotive components original equipment manufacturer and an aftermarket ride control and emissions products manufacturer. It is a Fortune 50 ...
, to create floating nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant (NPP) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power stations, heat is used to generate steam that drives a steam turbine connected to a electric generator, generato ...
s at the Port of Jacksonville
The Port of Jacksonville (Jaxport) is an international trade seaport on the St. Johns River in Jacksonville, Florida. The 14th largest container port in the United States, it carries about 18 million short tons of cargo each year and has an annu ...
.Adams, Rod"Offshore Power Systems: Big Plants for a Big Customer"
Atomic Insights, August 1996Putnam, Walter
"Floating nuclear plants may become reality"
Boca Raton News, November 15, 1981 Construction of the new facility was projected to cost $200 million and create 10,000 new jobs when completed in 1976."Urban waterfront lands"
Page 136, National Research Council Committee, 1980 Contracts were signed by
Public Service Electric and Gas Company
The Public Service Enterprise Group (PSEG) is a publicly traded diversified energy company headquartered in Newark, New Jersey and was established in 1985 with a legacy dating back to 1903.
The company's largest subsidiary is Public Service Elec ...
with PSE&G paying for the startup costs for the manufacturing facility.
Westinghouse named Zeke Zechella
Alexander Philip "Zeke" Zechella (August 11, 1920 – August 15, 2009) was a United States Navy veteran and pioneer in the usage of nuclear energy who headed several major companies before retiring in Jacksonville, Florida, and assisting local non ...
to be president of OPS in 1972.Kerr, Jessie-Lynne“ALEXANDER P. 'ZEKE' ZECHELLA: 1920-2009”
Florida Times-Union, August 18, 2009 OPS obtained 850+ acres (3.4 km2) on
Blount Island
Blount Island is an island of approximately on the St. Johns River in Jacksonville, Florida, nine nautical miles (16.7 km) west of the Atlantic Ocean. One of three public cargo facilities at the Port of Jacksonville is located there, and i ...
from the Jacksonville Port Authority
The Jacksonville Port Authority (JPA) also known by its brand name, JAXPORT, is the independent government agency in Jacksonville, Florida, that owns and operates much of the seaport system at the Port of Jacksonville.
History
The Jacksonville P ...
(JPA) for $2,000/acre, then installed infrastructure using over 1,000 workers. A total of $125 million was invested in the property and facility, however; no plants were ever built.
Ax Handle Saturday
Because of its high visibility and patronage, the Hemming Park and surrounding stores were the site of numerouscivil rights
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and political life of ...
demonstrations in the 1960s. Black Sit-in
A sit-in or sit-down is a form of direct action that involves one or more people occupying an area for a protest, often to promote political, social, or economic change. The protestors gather conspicuously in a space or building, refusing to mo ...
s began on August 13, 1960 when students asked to be served at the segregated lunch counter at Woolworths, Morrison's Cafeteria
Morrison's Cafeterias was a chain of cafeteria-style restaurants, located in the Southeastern United States with a concentration of locations in Georgia and Florida. Generally found in shopping malls, Morrison's primary competition was Piccadilly ...
and other eateries. They were denied service and kicked, spit at and addressed with racial slurs. This came to a head on "Ax Handle Saturday", August 27, 1960. A group of 200 middle aged and older white men (allegedly some were also members of the Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to the KKK or the Klan, is an American white supremacist, right-wing terrorist, and hate group whose primary targets are African Americans, Jews, Latinos, Asian Americans, Native Americans, and ...
) gathered in Hemming Park armed with baseball bats and ax handles. They attacked the protesters conducting sit-ins. The violence spread, and the white mob started attacking all African-Americans in sight. Rumors were rampant on both sides that the unrest was spreading around the county (in reality, the violence stayed in relatively the same location, and did not spill over into the mostly-white, upper-class Cedar Hills neighborhood, for example). A black street gang called the "Boomerangs" attempted to protect the demonstrators. Police, who had not intervened when the protesters were attacked, now became involved, arresting members of the Boomerangs and other black residents who attempted to stop the beatings.
Nat Glover
Nathaniel Glover Jr. (born March 29, 1943), is an American former college administrator and former police officer and sheriff. Glover is considered a pioneer in leadership in Jacksonville, Florida. He was the first African American elected sheriff ...
, who worked in Jacksonville law enforcement for 37 years, including eight years as Sheriff of Jacksonville, recalled stumbling into the riot. Glover said he ran to the police, expecting them to arrest the thugs, but was told to leave town or risk being killed.
Several whites had joined the black protesters on that day. Richard Charles Parker, a 25-year-old student attending Florida State University
Florida State University (FSU) is a public research university in Tallahassee, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida. Founded in 1851, it is located on the oldest continuous site of higher education in the st ...
was among them. White protesters were the object of particular dislike by racists, so when the fracas began, Parker was hustled out of the area for his own protection. The police had been watching him and arrested him as an instigator, charging him with vagrancy, disorderly conduct and inciting a riot. After Parker stated that he was proud to be a member of the NAACP
The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) is a civil rights organization in the United States, formed in 1909 as an interracial endeavor to advance justice for African Americans by a group including W. E.&nb ...
, Judge John Santora sentenced him to 90 days in jail.
Hurricanes
Jacksonville is one of the few cities on the Eastern coast that have been largely spared from the wrath ofhurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
s. Despite the damage and destruction that Hurricane Dora
Hurricane Dora was the first tropical cyclone on record to make landfall over the Atlantic coast of North Florida at hurricane intensity. The sixth tropical storm and second hurricane of the 1964 season, Dora developed from a tropical wave nea ...
caused in Jacksonville, the very next day, September 11, 1964, over 20,000 fans attended a live concert at the Gator Bowl Stadium
The Gator Bowl was an American football stadium in Jacksonville, Florida. Originally built in 1927, all but a small portion was razed in 1994 in preparation for the NFL's Jacksonville Jaguars' inaugural season; the reconstructed stadium became Jac ...
by the British rock-and-roll band, "The Beatles
The Beatles were an English Rock music, rock band, formed in Liverpool in 1960, that comprised John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr. They are regarded as the Cultural impact of the Beatles, most influential band of al ...
." The winds were blowing so hard that Ringo Starr
Sir Richard Starkey (born 7 July 1940), known professionally as Ringo Starr, is an English musician, singer, songwriter and actor who achieved international fame as the drummer for the Beatles. Starr occasionally sang lead vocals with the ...
's drumset had to be nailed down to the stage.
Dora was the only storm in recorded history to affect Jacksonville with hurricane-force winds, though the city has been affected by weaker storms as well as hurricanes that lost intensity before reaching the area. In September 1999, after Hurricane Floyd
Hurricane Floyd was a very powerful Cape Verde hurricane which struck the Bahamas and the East Coast of the United States. It was the sixth named storm, fourth hurricane, and third major hurricane in the 1999 Atlantic hurricane season. Floyd tr ...
struck the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to ...
, over one million Floridians were evacuated from coastal areas, many of them from Jacksonville. Mayor John Delaney announced the mandatory evacuation of the Jacksonville Beaches
The Jacksonville Beaches, or Jax Beaches known locally as "The Beaches", are a group of towns and communities on the northern half of an unnamed barrier island on the US state of Florida's First Coast, all of which are excluded cities or parts of ...
and other low lying neighborhoods early on September 14; in total, nearly 80,000 Jacksonville residents left their homes. Ultimately the storm turned northward 125 miles off the coast, causing only minor damage in Jacksonville and the southeastern US before making ground in North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
. In September 2017, Jacksonville experienced record flooding from Hurricane Irma
Hurricane Irma was an extremely powerful Cape Verde hurricane that caused widespread destruction across its path in September 2017. Irma was the first Category 5 hurricane to strike the Leeward Islands on record, followed by Maria two ...
.
Consolidation
Through the 1960s Jacksonville, like most other large cities in the US, suffered from the effects ofurban sprawl
Urban sprawl (also known as suburban sprawl or urban encroachment) is defined as "the spreading of urban developments (such as houses and shopping centers) on undeveloped land near a city." Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted growt ...
. To compensate for the loss of population and tax revenue and end waste and corruption, voters elected to consolidate the government of Jacksonville with the government of Duval County. The move was carried out on October 1, 1968, and Hans Tanzler
Hans Gearhart Tanzler, Jr. (March 11, 1927 – July 25, 2013) was an American politician and judge. He served as Mayor of Jacksonville, Florida from 1967 to 1979. During his administration, the City of Jacksonville consolidated with Duval Coun ...
, elected mayor of Jacksonville
The Mayor of Jacksonville is the chief executive for the city of Jacksonville, Florida, United States. Jacksonville currently utilizes the strong mayor form of government, in which the mayor has significant powers compared to the Jacksonville C ...
the year before, became the first mayor of the consolidated government. Jacksonville became the largest city in Florida and the 13th largest in the United States, and has a greater land area than any other American city outside Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
. All areas of Duval County are considered part of Jacksonville besides the four independent municipalities of Jacksonville Beach
Jacksonville Beach is a coastal resort city in Duval County, Florida, United States. It was incorporated on May 22, 1907, as Pablo Beach, and would later change its name to Jacksonville Beach in 1925. The city is part of group of communities col ...
, Atlantic Beach, Neptune Beach
Neptune Beach is a beachfront city east of Jacksonville in Duval County, Florida, United States. When the majority of Duval County communities consolidated with Jacksonville in 1968, Neptune Beach, along with Jacksonville Beach, Atlantic Beach ...
, and Baldwin, although residents of these towns vote in city elections and are eligible for services provided by Jacksonville.
Claude Yates
Claude J. Yates (December 26, 1899 - October 25, 1988), was a Jacksonville business executive in the 1960s who is known as the ''Father of Jacksonville's consolidation.''
Early years
Claude was born in Gibson County, Tennessee, the second of five ...
began the "quiet revolution" with the ''Yates Manifesto'' and J. J. Daniel was chairman of the ''Local Government Study Commission''. Lex Hester
Lewis Alexander Hester, III (December 24, 1935 – October 7, 2000) was a public administrator in Jacksonville, Florida. He "was the consummate no-nonsense administrator, the very best in his field," according to M. C. Harden III, past chairman of ...
was Executive Director of the commission and the key architect of Jacksonville's consolidated government, transition coordinator and chief administrative officer following consolidation.
See also
* List of people from Jacksonville, Florida *Timeline of Jacksonville, Florida
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Jacksonville, Florida, USA.
Prior to 20th century
* 1564 - French Fort Caroline established by René Goulaine de Laudonnière.
* 1565 - Spanish forces take Fort Caroline.
* 1822
** Set ...
* History of African Americans in Jacksonville
References
Bibliography
* Bartley, Abel A. ''Keeping the Faith: Race, Politics, and Social Development in Jacksonville, Florida, 1940–1970.'' (2000). 177 pponline edition
External links
Photographic exhibit on the Great Fire of 1901; presented by the State Archives of Florida.
The Jacksonville Historical Society
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Jacksonville, Florida